Regardless of the manufacturer, all the Process Analytical Technology (PAT) probes used for absorption spectroscopy must be periodically cleaned, serviced, and referenced or zeroed. The periodic maintenance schedule can range from weeks to several months depending upon the instrument and process stream conditions.
Consequently, practical methods for removal of the probe from the process, access to the windows, or complete disassembly and reassembly abilities are often desirable features to look for when choosing new sample interfaces. For direct insertion probes, the type of seal to the pipeline or reactor determines the effort required to service. The three main ways a direct insertion probe can be sealed to a process are; welded flange onto the probe body, a mechanical extractor with gate value, or a Swagelok™ fitting. For flow cells, some companies offer cleaning ports to facilitate this maintenance without requiring the probe to be disconnected from the process line.
Maintenance – Consider Usability
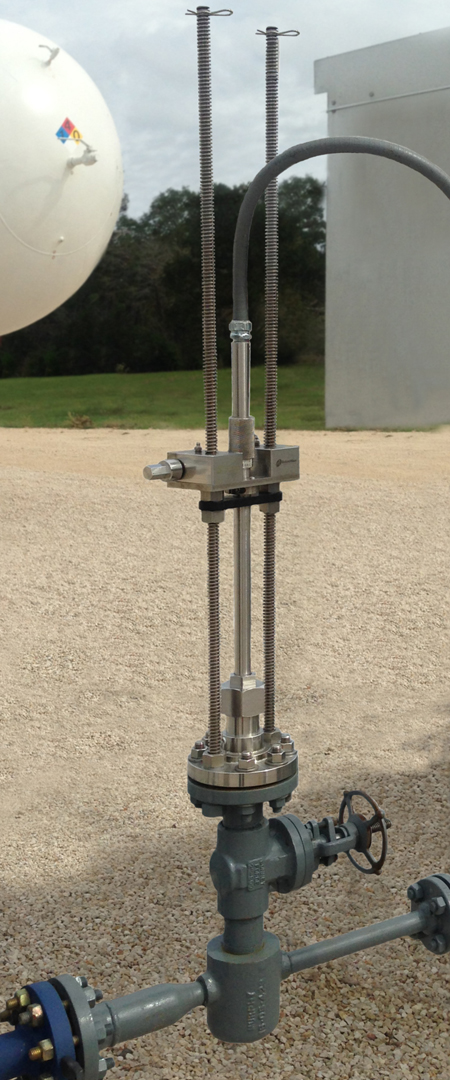

Extractor Mechanism
For faster removal and servicing of insertion probes without shutting down the process, using a probe extractor mechanism will pay for itself quickly.
The Probe Extractor Mechanism is used for the controlled extraction/insertion of an in-line probe from pressurized process streams or reactors for servicing. Coupled with a gate or ball valve, these extractors have proven safe and effective in a variety of installations. Watch the Probe Extractor Mechanism in Action
Faster Removal and Servicing of Insertion Probes without Shutting Down the Process
The Probe Extractor Mechanism utilizes a pneumatic drill to extract and insert the probe from the assembly via a gear mechanism. It may also be operated by a hand-held crank if drills are not permitted in the areas.
When the Probe Extractor Mechanism is purchased with a Guided Wave insertion probe, it’s conveniently assembled at their factory prior to shipment. This allows installation in the field to be fast and uncomplicated. Shutting down the process just to remove the probe and clean the windows is not possible for most plants. Installing the Probe Extractor Mechanism allows maintenance of the probe while the process is running, proving continuous use of the analyzer to verify process quality.
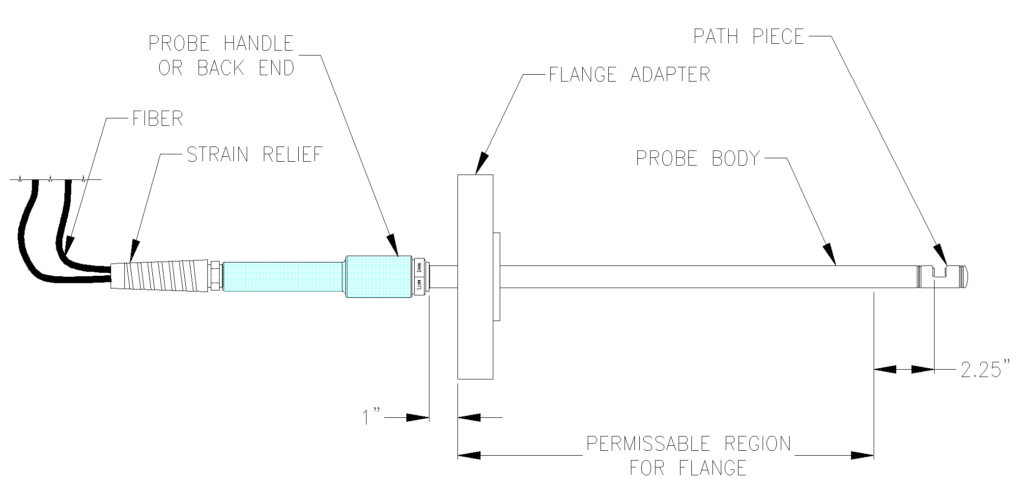
Flanged Probe
A custom flange can be welded onto the body of the insertion probe. The flanged probe can then be bolted onto the process line or reactor. The flanged probe is ideal for high temperature or pressure applications where the probe will only need to be serviced during plant shutdowns.

Swagelok™ Connectors
For low-pressure applications, a direct insertion probe can be connected with either Swagelok™ with Teflon™ ferrules or Swagelok™ Tube Fittings. In either case, the probe can only be removed for service when the process is offline.
Process Analytical Technology
Process analytical technology (PAT) is defined by the FDA as a mechanism to design, analyze, and control pharmaceutical manufacturing processes through the measurement of critical process parameters that affect critical quality attributes of an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).